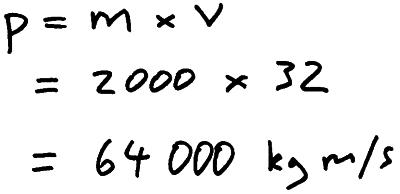Momentum Momentum = mass x velocity ( Kgm/s ) (kg) (m/s) If an object is moving towards you, your safety will depend on * how massive the object is * how. - ppt download
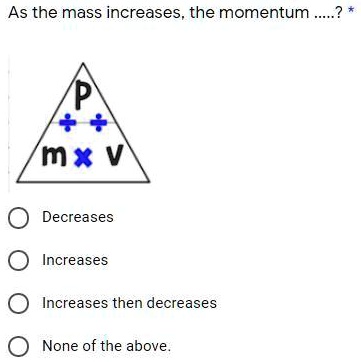
SOLVED: 'Please help extra points!!!! As the mass increases, the momentum + P mxV Decreases Increases Increases then decreases None of the above.'

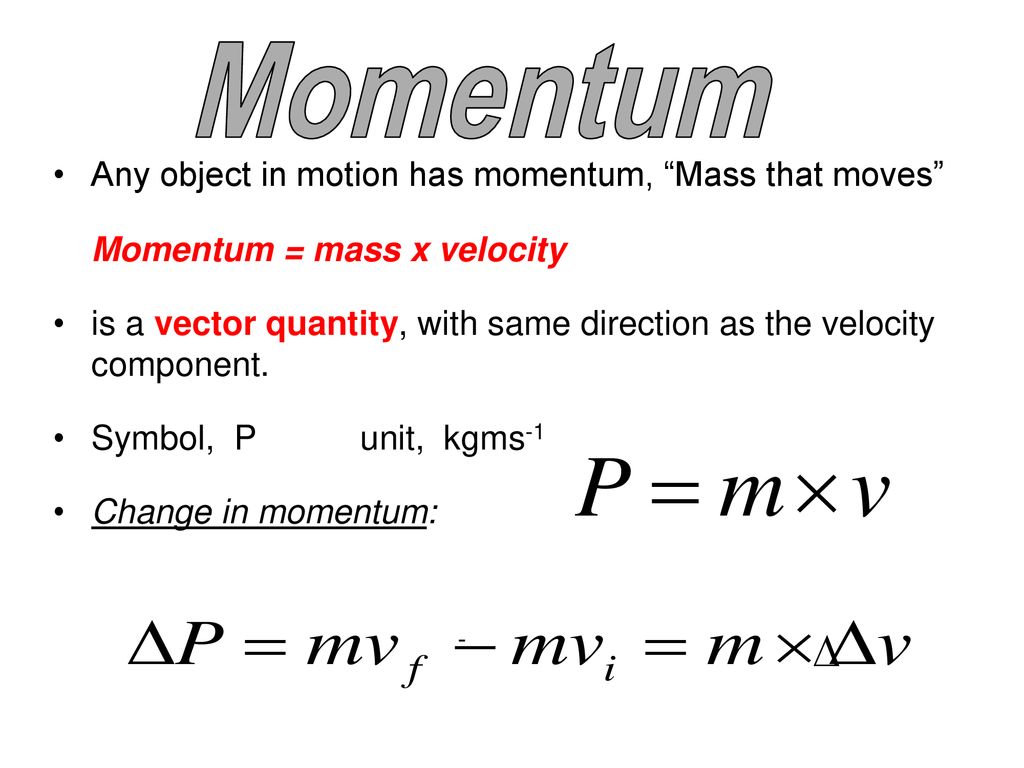
MOMENTUM. Specification Forces and motion Forces, movement, shape and momentum know and use the relationship: momentum = mass × velocity p = m × v use. - ppt download

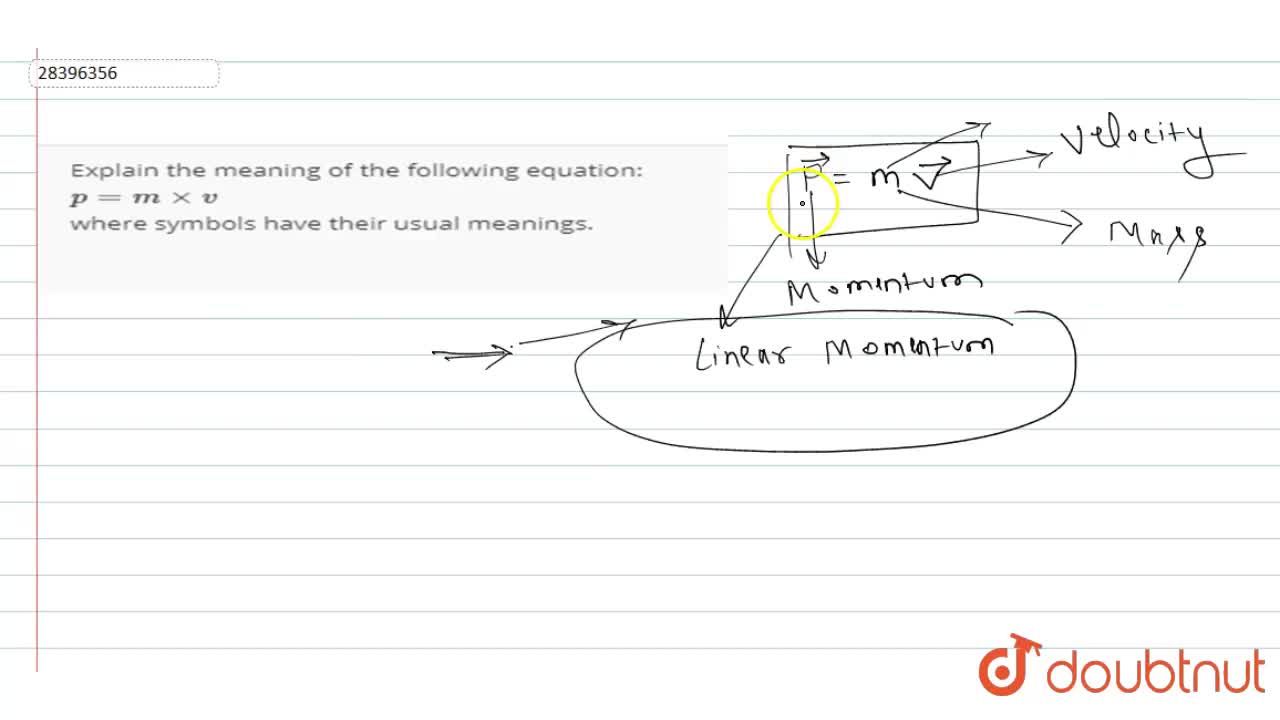
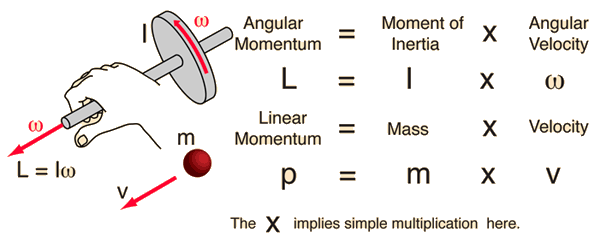
MOMENTUM. DEFINITIONS Linear momentum (p) is defined as the product of mass (m) and velocity (v): p = m x v SI-unit of momentum is 1 kg ∙ m ∙ s -1, alternative. - ppt download

Unit 4: Momentum & Impulse I can calculate momentum using p=mv I can calculate impulse using I = Ft. - ppt download